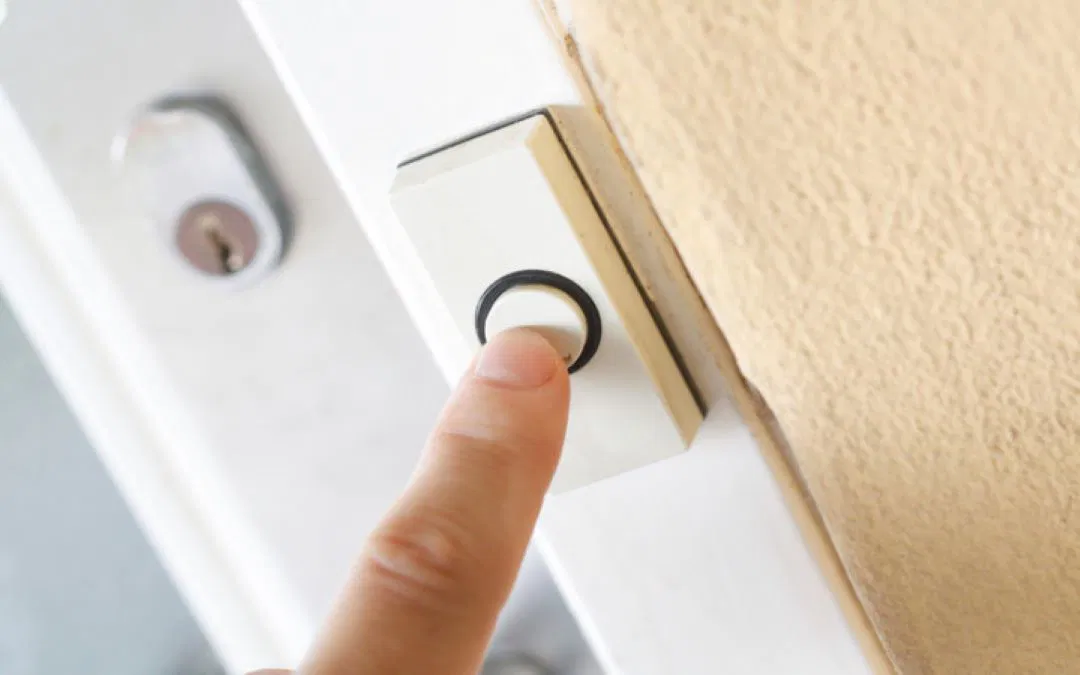

Do you ever wonder how a doorbell works? It might seem simple, but there's a lot of science and engineering behind it. A doorbell typically uses a combination of a transformer, solenoid, and electromagnet to create sound or light when the button is pressed.
In traditional wired doorbells, pressing the button completes an electrical circuit, allowing current to flow through wires to a terminal that activates the bell or chime, resulting in the familiar "ding" or "ring" sound. This system relies on a low-voltage power source, usually provided by a transformer that reduces the household voltage to a safer level for the doorbell.
Wireless doorbells, on the other hand, use radio signals to trigger the sound. When the button is pressed, it sends a signal to a receiver connected to the chime or bell, which then produces the sound. These systems are often battery-powered, making them easy to install without the need for complex wiring.
Whether it's a classic mechanical bell or a modern electronic chime, understanding how a doorbell works involves knowing the basics of electricity, magnetism, and mechanical movement. If any part of the system fails, such as the switch, wire, or circuit, it may need to be replaced to ensure the doorbell continues to function properly.
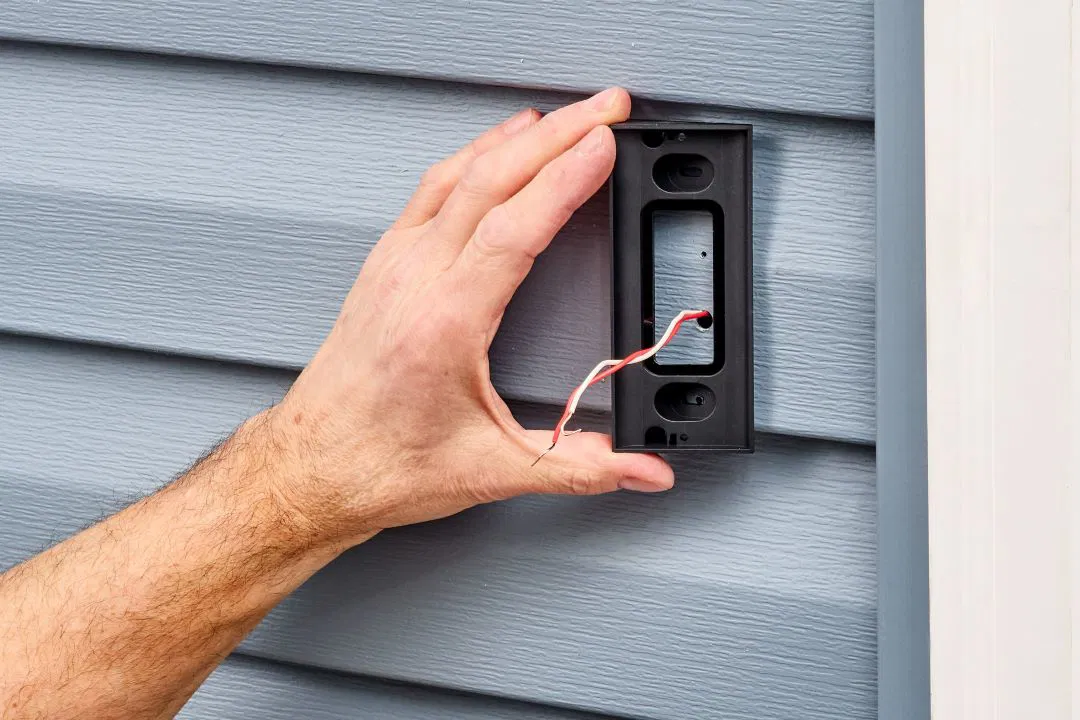

How Does an Electric Wired Doorbell Work?
An electric wired doorbell operates by completing an electrical circuit when the button is pressed. This allows current to flow from the transformer through the wires to the chime or bell, producing the characteristic "ding" or "ring" sound. Some models also include a light that illuminates to indicate the button has been pressed. These systems are usually powered by either batteries or connected to the home’s electrical system.
If you're curious about what happens when the doorbell rings, it's all about the flow of electricity through the wires. Keeping your doorbell in good working condition is important for both convenience and security. Regular maintenance or replacement of faulty components can help ensure it functions correctly over time.
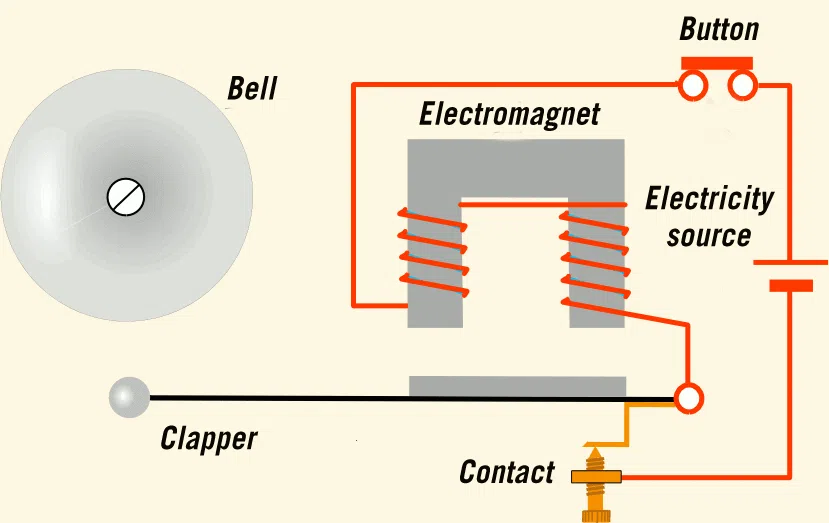
How a Doorbell Works: Electromagnetic Principle
A doorbell works by using the principle of electromagnetism. When the button is pressed, it closes the circuit, allowing current to flow through a transformer. This activates a solenoid with an iron core, which generates a magnetic field. This magnetic force pulls a striker or hammer, causing it to hit the bell or chime and produce sound.
In wired systems, the button acts as a switch that allows power from the transformer to move through the circuit. The transformer plays a key role by reducing the high voltage from your home’s electrical system to a lower, safer level for the doorbell. In wireless systems, the button sends a signal to a receiver, which then triggers the sound mechanism.
Wireless doorbells offer greater flexibility in installation since they don’t require extensive wiring. They’re ideal for homes where running wires isn’t practical. Whether wired or wireless, the basic principle remains the same: a simple push of a button sets off a chain of events that results in a sound alerting you to someone at the door.
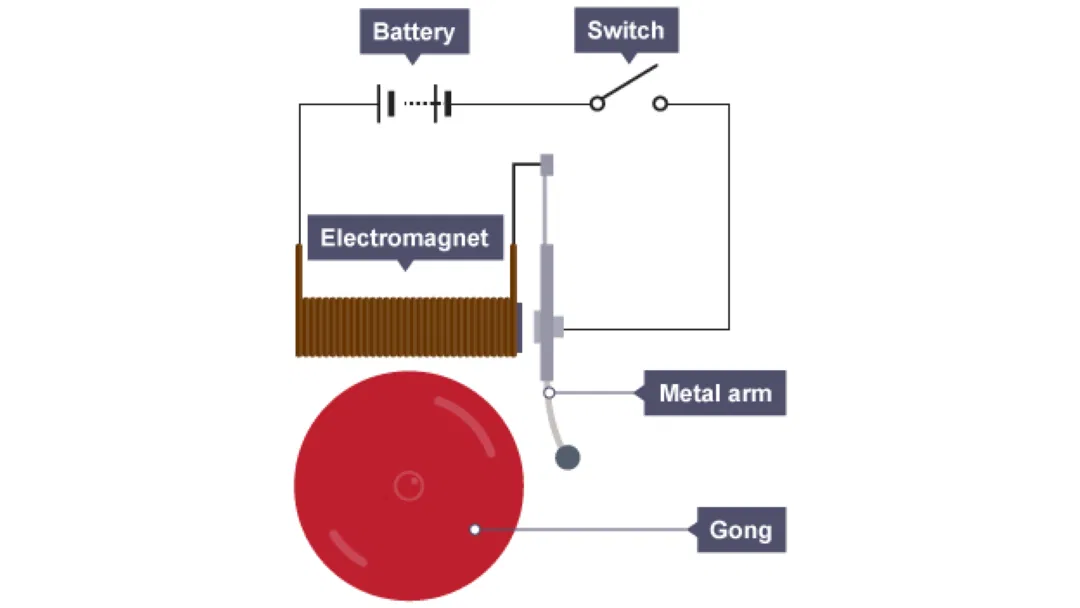
How Does an Electric Doorbell Work?: Doorbell Physics
An electric doorbell works by creating sound through an electrical circuit. When the button is pressed, it closes the circuit, allowing current to flow from the transformer through the wires to the chime or bell unit. This current generates a magnetic field within the solenoid, pulling a striker or hammer to hit the tone bars or bells, producing the distinct ringing sound.
The transformer is essential in this process, as it steps down the high voltage from the main power supply to a lower, safe voltage suitable for the doorbell system. An electric doorbell typically consists of several key parts: the button, the transformer, the solenoid with an iron core, and the chime or bell unit.
The button, located at the entrance, acts as a switch to activate the circuit. When pressed, it allows the current to travel from the transformer’s secondary terminals through the solenoid to the chimes, creating sound. These systems are commonly used not only in homes but also in schools, public buildings, and smart doorbells, which integrate advanced features like video and audio capabilities.
In summary, doorbells operate through the interaction of electric current, magnetic fields, and mechanical movement, resulting in the pleasant chimes we hear when someone is at the door.
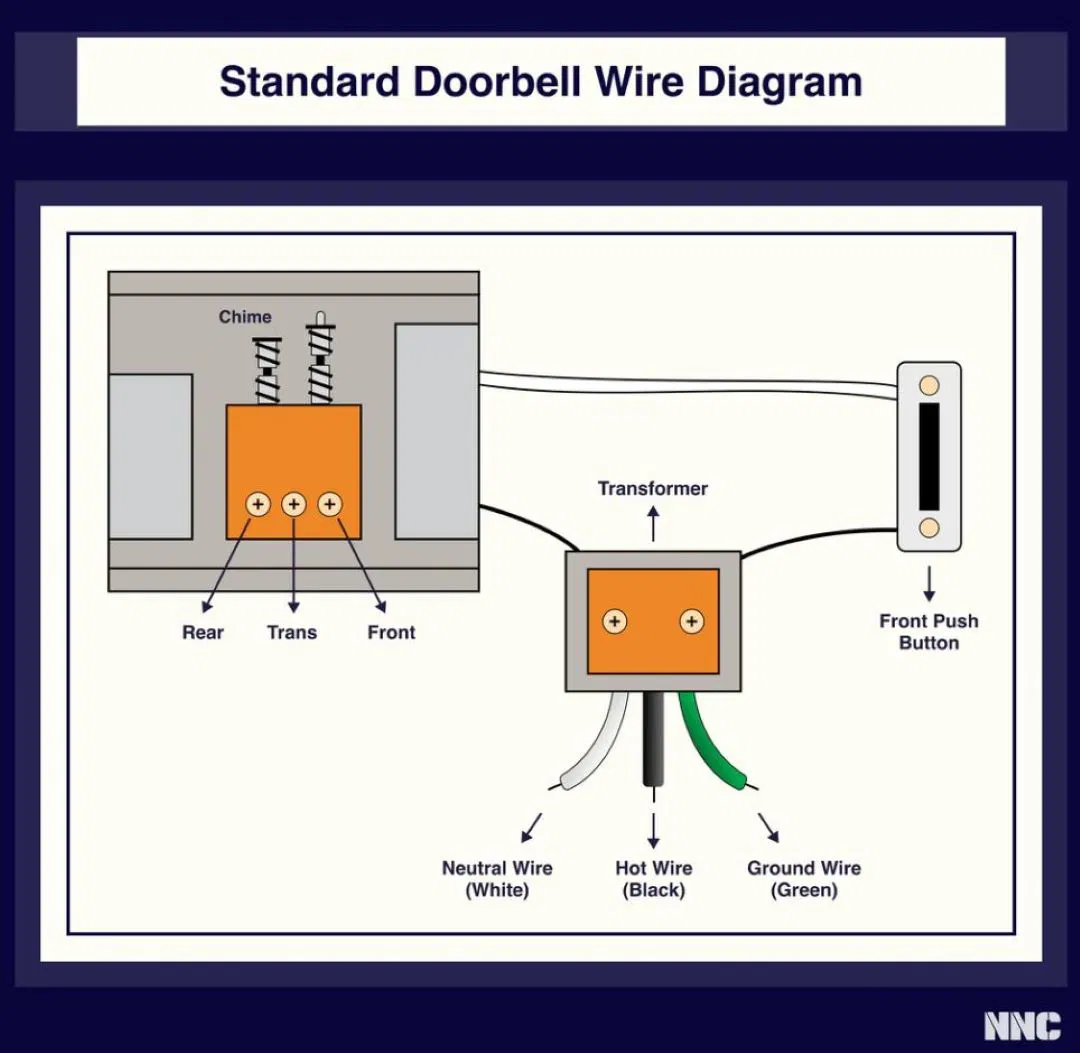
How Does a Doorbell Work?: Doorbell Wiring Diagram
A doorbell works when you press the button, whether it's wired or wireless. Pressing the button allows current to flow through the solenoid, generating a strong magnetic field that pulls an iron rod toward the bell or chime, causing it to strike and produce sound.
A standard wired doorbell wiring diagram includes connections between the button, the transformer, and the chime or bell. Two wires connect the button to the transformer and then to the chime unit. When the button is pressed, the circuit is completed, and the chime sounds a "ding dong" noise.
For a Ring doorbell, the setup may involve more complex connections, especially if it's a smart system integrated with your phone for notifications. These systems often include video and audio features. A simple doorbell circuit diagram shows the basic components necessary for the system to function, including the button, transformer, and chime unit.
Older doorbell systems typically use four wires, while newer, battery-powered models often use just two. The number of wires depends on the complexity of the chime pattern or additional features. Regardless of the system, the core concept remains the same: pressing the button completes the circuit and triggers the sound.
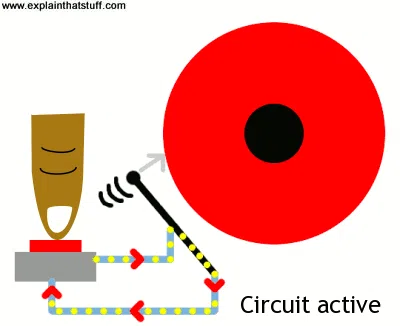
How Does an Electric Doorbell Work?: Electric Doorbell Animation
An electric doorbell works by using electromagnetism to generate sound. When the button is pressed, it closes the circuit, allowing current to flow from the power source through the system. This current passes through a transformer, which adjusts the voltage to the required level for the doorbell.
The current then moves through wires connected to the solenoid. The solenoid, made of a coil of wire and an iron core, becomes magnetized when the current flows through it, turning into an electromagnet. This electromagnetic force causes the iron core to move, triggering a mechanical action that strikes the bell and creates the familiar "ding dong" sound.
Once the button is released, a spring pushes the iron core back to its original position, ready for the next activation. In a wired doorbell, the components are connected by two wires running from the button to the transformer and solenoid. Some systems also include a light to indicate when the button is pressed, adding an extra visual cue.
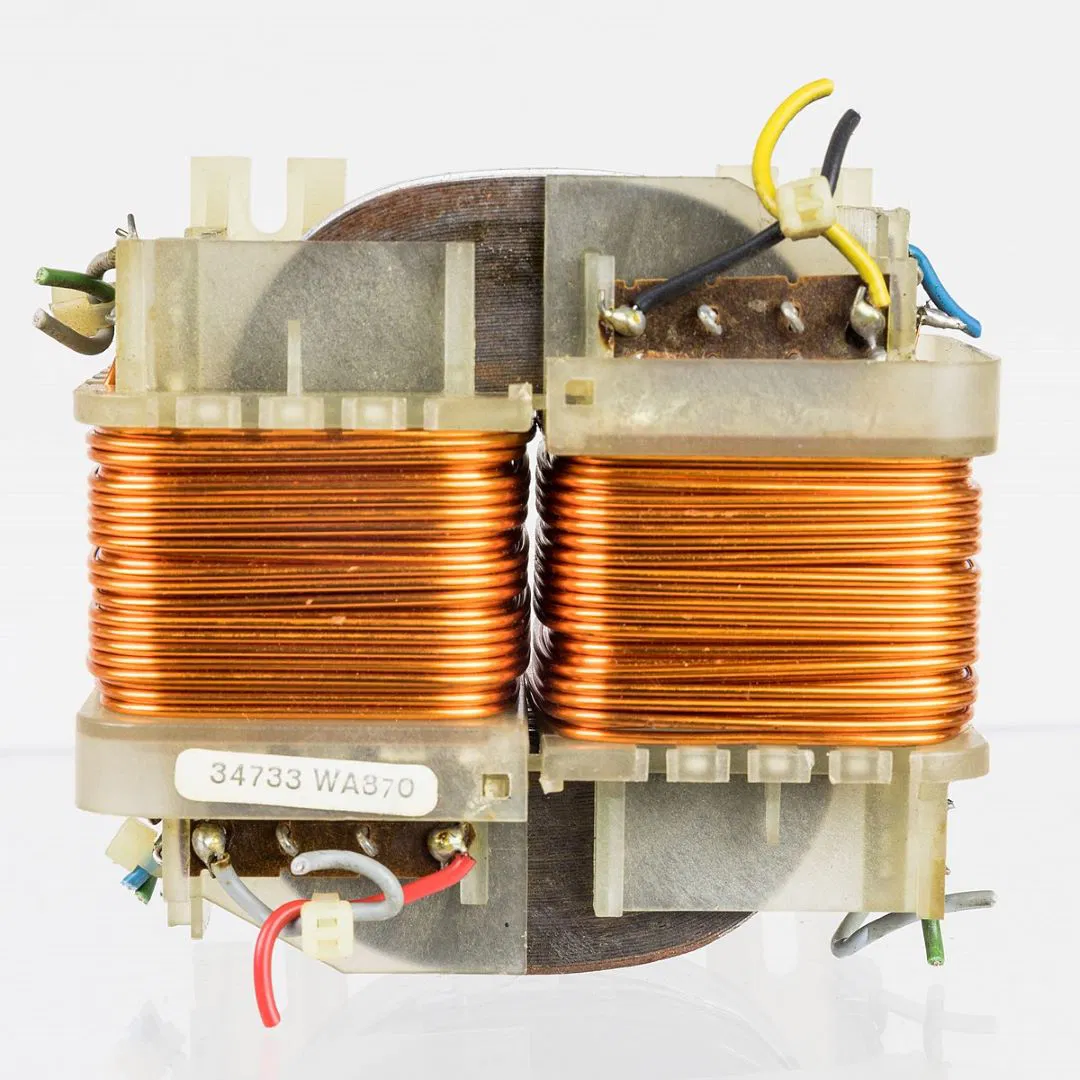
Where Does a Doorbell Get Its Power From?
A doorbell gets its power from the home's electrical system through a transformer, which reduces the high voltage to a safer level for the doorbell. In wired systems, pressing the button completes the circuit, allowing electricity to flow through two wires to the doorbell's terminals, triggering the chime at the front door.
The switch mechanism in the doorbell is simple yet effective, ensuring the circuit is completed each time it's pressed. The transformer plays a vital role in this process by converting the household voltage to a lower, manageable level for the doorbell. Wireless doorbells, on the other hand, rely on batteries and radio signals, eliminating the need for direct electrical connections.
Wireless doorbells are available as smart video doorbell cameras, offering additional features like video monitoring and smartphone connectivity. Whether wired or wireless, the interaction between electricity and the doorbell circuit is fundamental to generating the sounds heard when someone is at the door.
How Does a Doorbell Make Sound?: Doorbell Chime Sound
A doorbell produces sound by using the magnetic field from an electromagnet to activate a mechanism that rings the chime. When the button is pressed, an electric current flows through the wire, activating the solenoid in the electromagnet.
This magnetic field attracts a metal striker or hammer, which hits the bell or tone plate, producing the familiar "ding dong" sound. The button press triggers this process, causing the striker to hit the chimes in succession, resulting in the ringing sound we hear. The doorbell chime relies on this precise flow of electric current and magnetic force to signal someone’s presence effectively.
If your doorbell isn't producing any sound, it might be faulty. Discover the reasons your doorbell is not working.

Does a Doorbell Work Without Electricity?
Yes, a doorbell can work without electricity, especially with modern wireless models. These systems operate on batteries and do not require a transformer or traditional electrical connection. They are designed to function independently, making installation easier and more flexible.
When the button is pressed, a signal is transmitted from the button to the chime unit, which is powered by the internal battery. This process triggers the sound mechanism, often mimicking the traditional chime without the need for direct electrical current or high voltage.
Smart doorbells enhance this by incorporating features like video cameras and smartphone connectivity, allowing users to see and speak with visitors remotely. Thus, the role of the transformer becomes obsolete in these systems, creating a more convenient and user-friendly solution for home security and convenience.
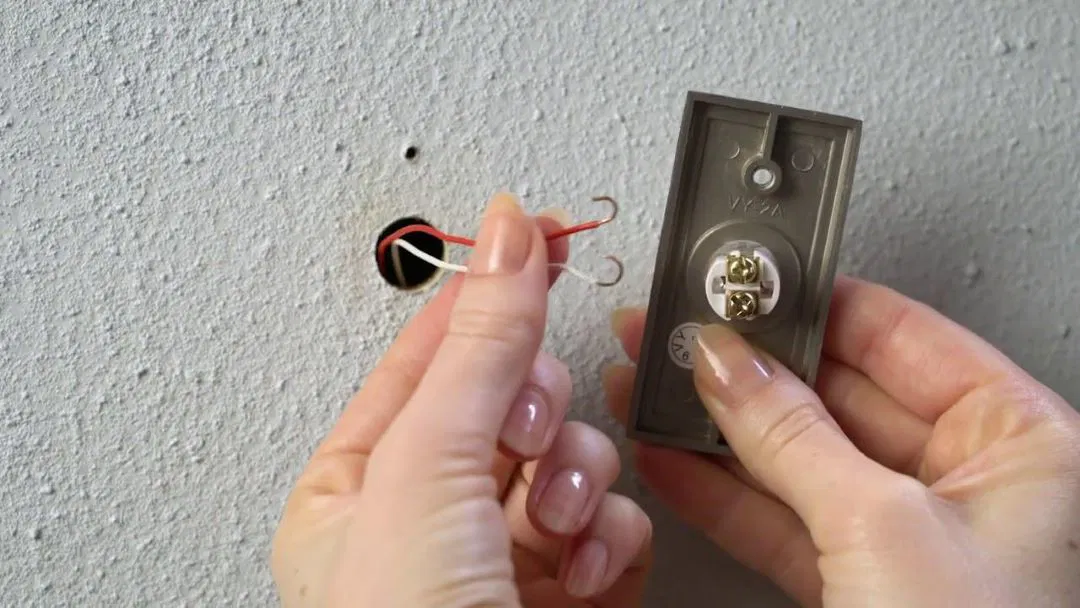

Is It Safe to Touch Doorbell Wires?: Wired Doorbells Safety
Yes, it is generally safe to touch doorbell wires, as they typically operate on low voltage, which minimizes the risk of shock. The electricity flowing through these wires is usually around 16 to 24 volts, significantly lower than the standard house voltage of 120 to 240 volts.
However, it's still important to exercise caution. Always make sure the power is turned off before handling or replacing doorbell components to eliminate any risk entirely. Even though the low voltage makes it safer, improper handling can lead to minor shocks or damage to the wiring.
Always double-check power sources and follow safety guidelines to ensure the process of replacing or working with doorbell wires is completely secure. If you're unsure, it's best to consult a professional. For more information on doorbell installation, contact Lito Electrical Service or learn how to replace a doorbell switch.
Bright Silver Polypropylene Label
Bright Silver Polypropylene Label,Metallised Bopp Label,Metallised Bopp Sticker,Metallised Pp Sticker
SOONTOMAX (TAISHAN) LABEL MATERIAL CO.LTD , https://www.stmlabel.com