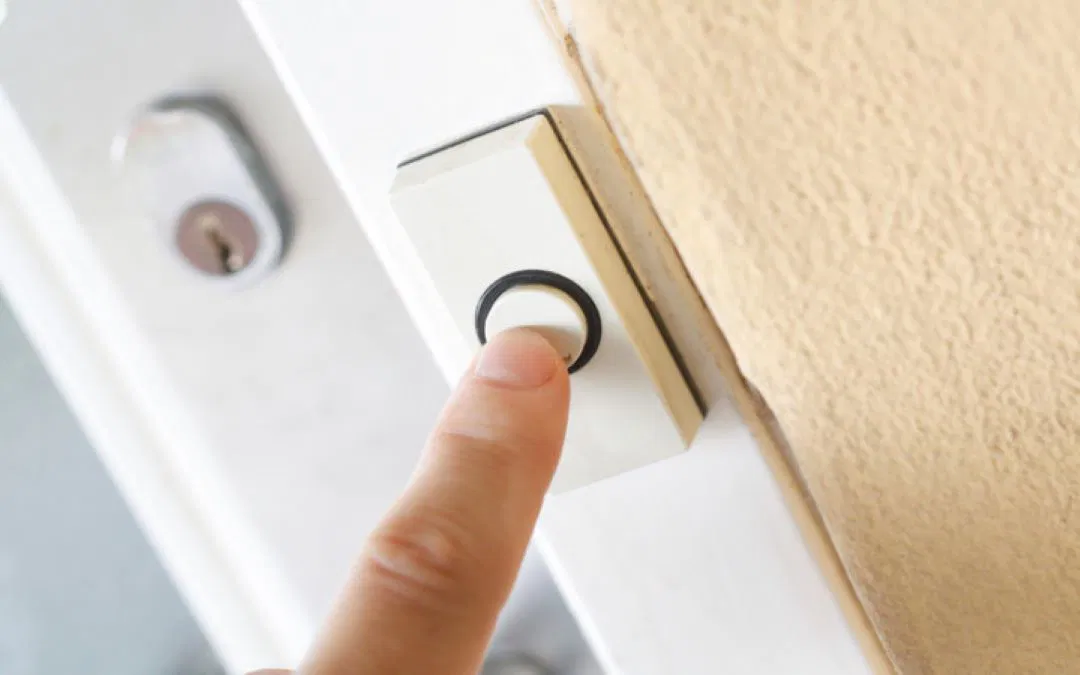

Do you ever wonder how your doorbell works when someone presses the button? It might seem simple, but there's actually some fascinating science and engineering behind it. A doorbell typically uses electromagnetism, a transformer, and a solenoid to create sound or light when activated.
In traditional wired doorbells, pressing the button completes an electrical circuit. This allows current to flow through wires to a terminal that activates a bell or chime, producing the classic "ding" sound. The system is usually powered by a low-voltage transformer connected to your home’s main electricity supply.
Wireless doorbells operate differently. Instead of wires, they use radio signals to trigger the sound. When the button is pressed, it sends a signal to a receiver, which then activates the chime or bell. Some models even include lights to indicate that the signal has been received.
Whether it's a classic bell or a modern electronic version, the basic principle remains the same: electricity flows through a circuit, activating a mechanism that creates sound. If any part of the system fails, such as the button, wire, or transformer, it can stop working. In such cases, replacing the faulty component is usually necessary to restore function.
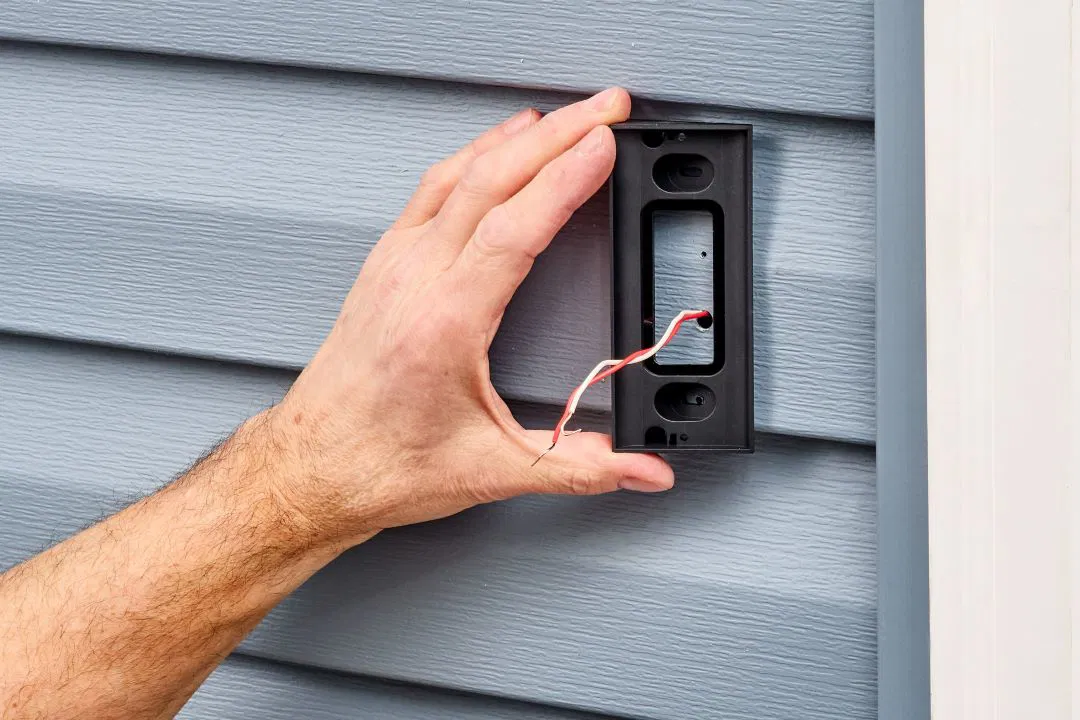

How Does an Electric Wired Doorbell Work?
An electric wired doorbell functions by completing an electrical circuit when the button is pressed. This allows current to flow from the transformer through the wiring to the chime or bell, producing the familiar "ding" or "ring" sound. Some systems also have a light that turns on to indicate the button was pressed.
The system is usually powered by either batteries or connected directly to your home's electrical system. Understanding how the switch, wires, and circuit work together is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining your doorbell. If something goes wrong, it's important to identify the issue early to avoid further damage.
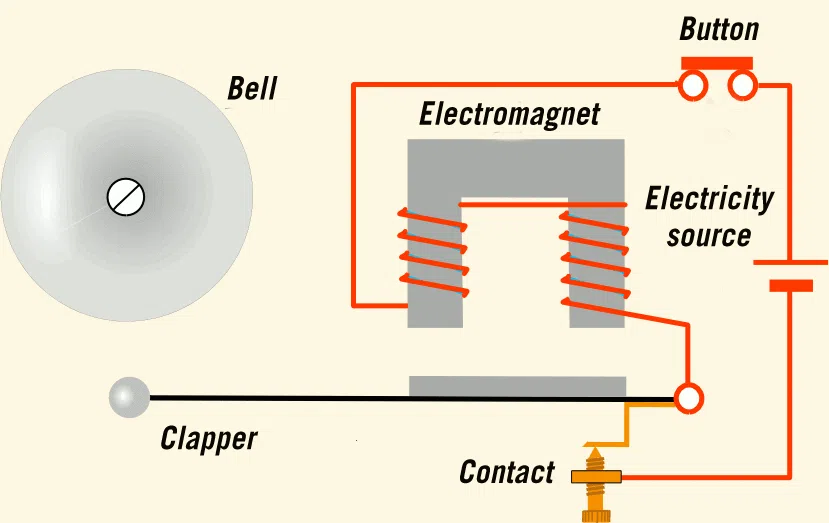
How a Doorbell Works: Electromagnetic Principle
A doorbell works based on electromagnetic principles. When you press the button, it closes a circuit, allowing current to flow through a transformer. This activates a solenoid with an iron core, which generates a magnetic field that pulls a striker to hit the bell or chime.
The transformer is key in this process, as it reduces the high voltage from your home's power supply to a lower level suitable for the doorbell. In wireless models, the button sends a signal via radio waves to a receiver, which then triggers the sound mechanism. These systems offer more flexibility in installation since they don't require extensive wiring.
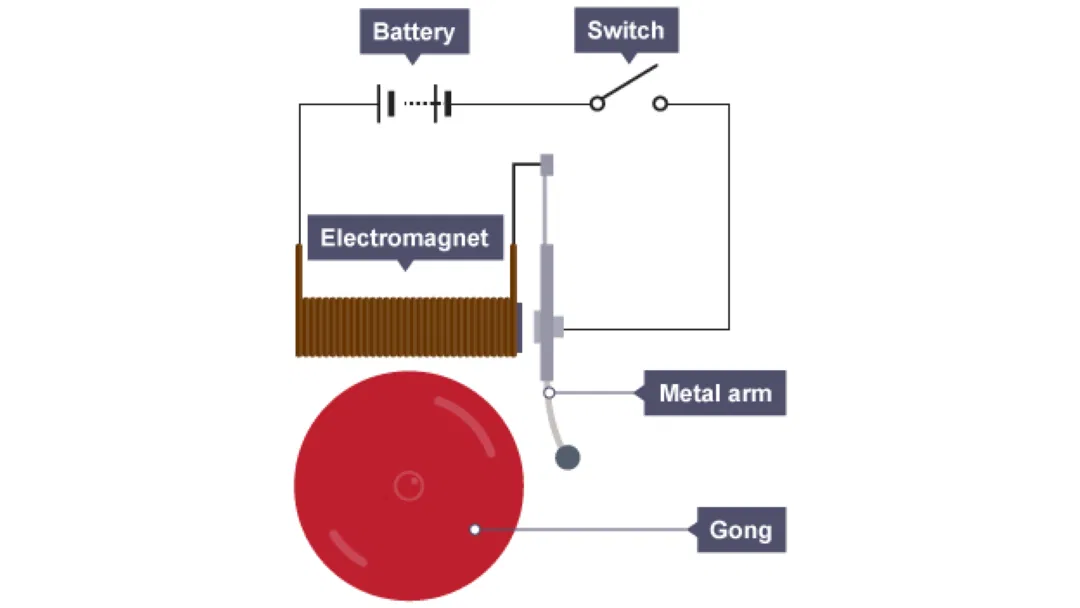
How Does an Electric Doorbell Work?: Doorbell Physics
Electric doorbells rely on the interaction between electricity, magnetism, and mechanical movement. When the button is pressed, it closes the circuit, allowing current to flow from the transformer through the wires to the chime unit. This current energizes a solenoid, creating a magnetic field that pulls a striker to hit the bell or tone bars, producing the distinctive "ding dong" sound.
The components of an electric doorbell typically include the button, transformer, solenoid, and chime unit. The button acts as a switch, while the transformer ensures the correct voltage is used. These systems are widely used in homes, schools, and public buildings, with smart doorbells adding features like video and audio capabilities for enhanced security.
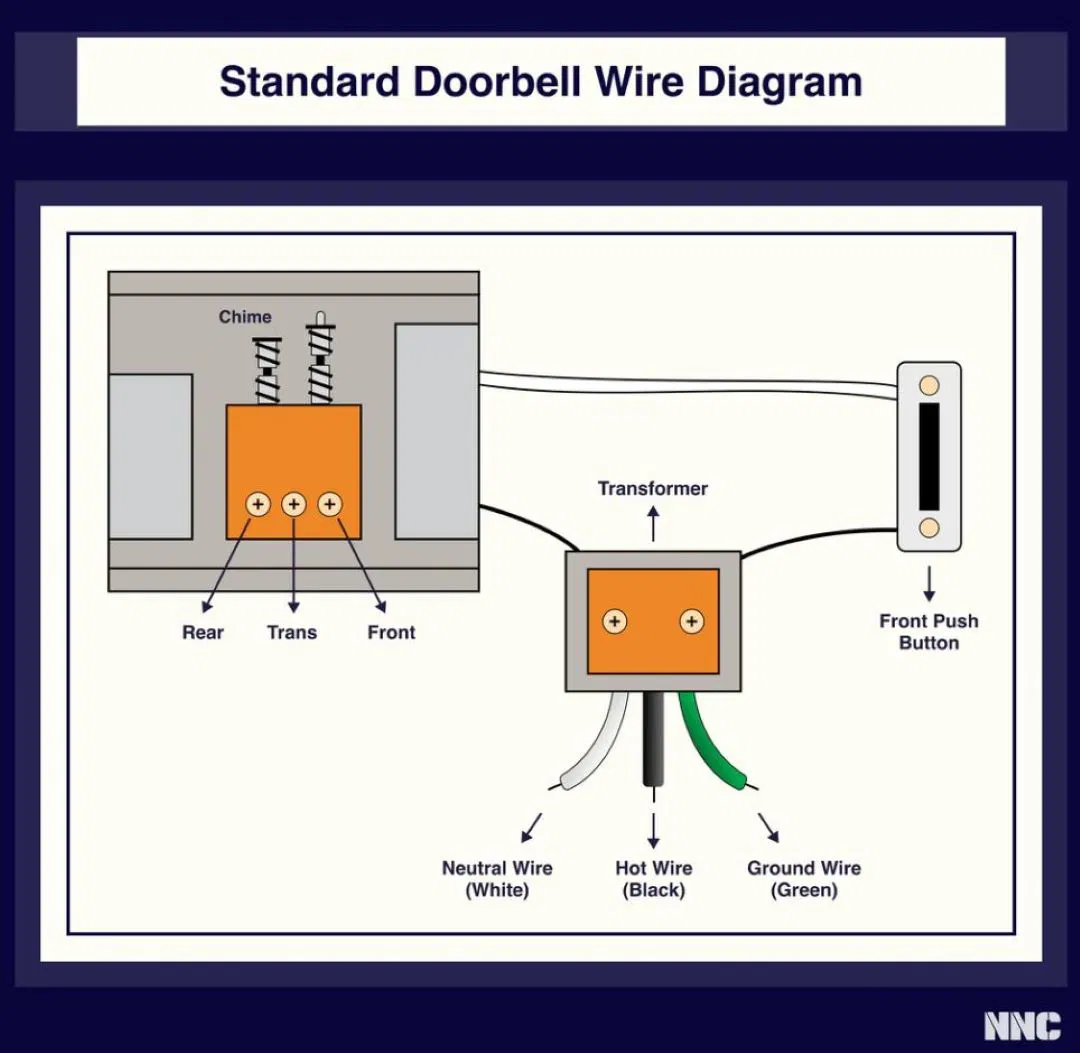
How Does a Doorbell Work?: Doorbell Wiring Diagram
A doorbell works by completing an electrical circuit when the button is pressed. In wired systems, two wires connect the button to the transformer and the chime unit. Pressing the button allows current to flow, triggering the chime. For smart doorbells, the wiring may be more complex, involving integration with phone apps and other devices.
Older doorbell systems often use four wires for more complex chime patterns, while newer battery-powered models typically use just two. Regardless of the setup, the basic principle remains the same: pressing the button completes the circuit and activates the sound mechanism.
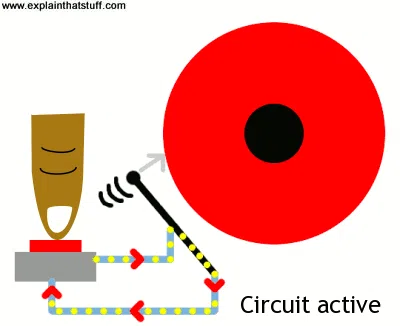
How Does an Electric Doorbell Work?: Electric Doorbell Animation
An electric doorbell works using electromagnetism. When the button is pressed, current flows through the system, passing through a transformer that adjusts the voltage. The current then moves through wires connected to a solenoid, which becomes an electromagnet when activated.
This magnetic force pulls an iron core, causing a mechanical action that strikes the bell and produces the familiar "ding dong" sound. Once the button is released, a spring returns the core to its original position. In wired systems, the components are connected by two wires running from the button to the transformer and solenoid.
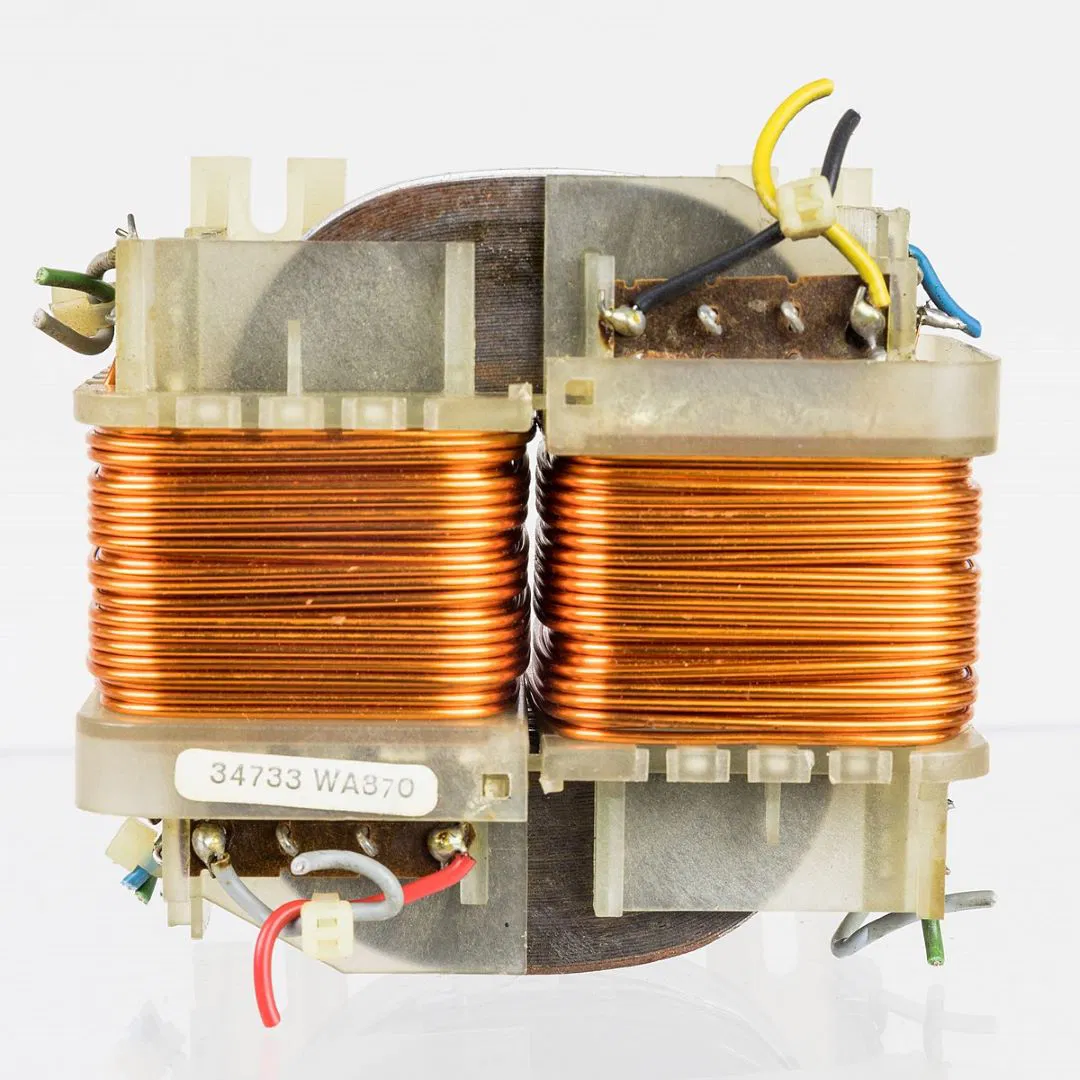
Where Does a Doorbell Get Its Power From?
A doorbell gets its power from the home's electrical system through a transformer, which reduces the voltage to a safe level for the doorbell. In wired systems, pressing the button completes the circuit, allowing electricity to flow through two wires connected to the terminals.
This triggers the bell to ring. The transformer plays a crucial role in converting the household voltage to a lower one for the doorbell. Wireless doorbells, on the other hand, use batteries and radio signals instead of direct electrical connections.
How Does a Doorbell Make Sound?: Doorbell Chime Sound
A doorbell makes sound by using an electromagnet to activate a mechanism that rings the chime. When the button is pressed, current flows through the wire, activating the solenoid. This magnetic field attracts a metal striker, which hits the bell or tone plate, creating the "ding dong" sound.
The process is repeated each time the button is pressed, making the chime work effectively. If your doorbell isn’t working, it could be due to a faulty component, so checking the wiring and connections is essential.

Does a Doorbell Work Without Electricity?
Yes, a doorbell can work without electricity, especially if it's a wireless model. These systems run on batteries and do not need a transformer or direct connection to your home's power supply.
When the button is pressed, it sends a signal to the chime unit, which is powered by the internal battery. This allows the doorbell to produce sound without requiring a constant electrical source. Smart doorbells take this concept further by adding features like video cameras and smartphone connectivity.
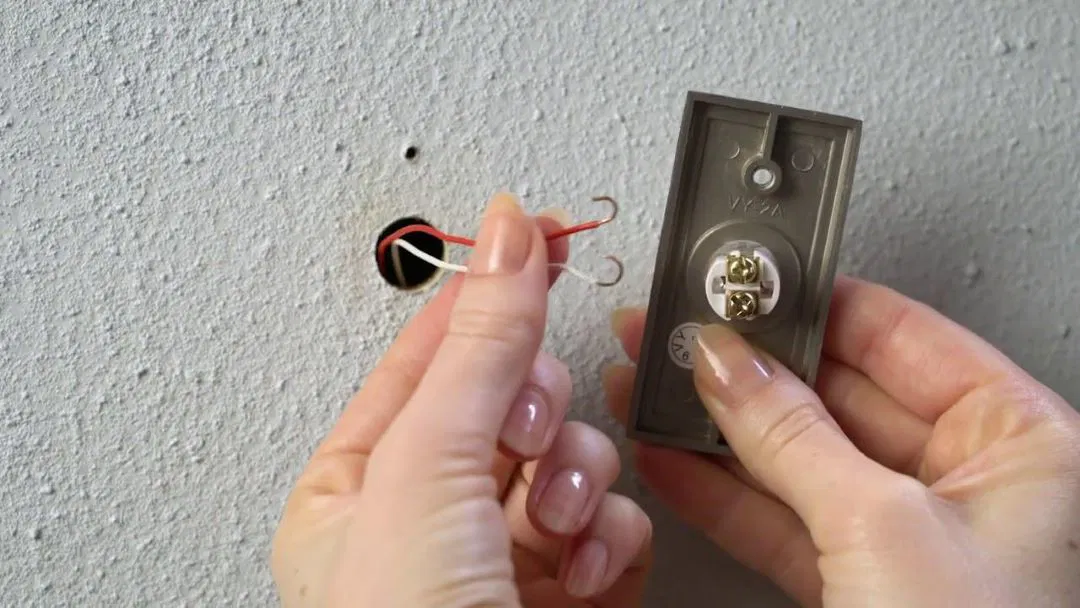

Is It Safe to Touch Doorbell Wires?: Wired Doorbells Safety
Touching doorbell wires is generally safe because they operate at low voltage—usually around 16 to 24 volts. This is much safer than standard household voltages of 120 to 240 volts. However, it's still important to turn off the power before working on them to prevent any accidental shocks.
While the risk is low, improper handling can still cause minor issues. Always follow safety guidelines and double-check the power sources before performing any maintenance. If you're unsure, it's best to consult a professional electrician.
Silver Foil Label,Silver Foil Sticker,Aluminum Foil Lable,Bright Silver Aluminum Foil Paper
SOONTOMAX (TAISHAN) LABEL MATERIAL CO.LTD , https://www.stmlabel.com